If your website opens very slowly in the browser and pages take a long time to load, even though you’re using fast hosting server, then your DNS might be slow.
A slow DNS lookup can reduce website page loading speed by 20% to 40%, as HTML, CSS, or JavaScript cannot be downloaded until the DNS resolution is complete.
In this article, I will tell you how to fix slow dns lookup, how to flush dns cache, and how to reduce dns lookups in WordPress with practical examples.

Imagine that if the DNS lookup is slow, everything else is forced to wait until the DNS is resolved, no server response, no rendering, and no user interaction.
This is why even websites with powerful hosting and optimized code can appear slow due to slow DNS lookups, and you might be experiencing this problem too.
Today I’m going to tell you the solution to this problem.
What Is a DNS Server?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the internet’s phonebook. It is the process of translating a domain name into an IP address.
Browsers cannot connect to domain names, they connect only to IPs, whenever you open a website in your browser, your computer needs the website’s actual IP address.
For Example:
You type a website URL (such as mozedia.com) into your internet browser, and the DNS then translates it into 135.184.216.240 (an example IP address).
What is DNS Lookup Time?
DNS lookup time is the time it takes between sending a DNS request and receiving a valid IP response.
Based on extensive testing and production data. According to Chrome DevTools documentation.
- < 50 ms – Excellent
- 50–100 ms – Acceptable
- 100–200 ms – Performance warning
- 200 ms+ – Critical issue
If the DNS lookup is taking 200 to 300ms or more, it is negatively impacting your website’s speed. You should investigate this and fix it.
Why Slow DNS Lookup Hurts Performance?
DNS delays are uniquely damaging because they occur before parallelization, as explained in Google’s web performance guidelines .
Unlike images or scripts, which can be downloaded concurrently, DNS resolution is a blocking process.
Until DNS completes:
- No server handshake starts
- No HTTP requests are issued
- No rendering begins
This leads to:
- Increased TTFB
- Poor Core Web Vitals
- Higher bounce rates
- Lower perceived speed
From a performance perspective, DNS is a single point of failure.
Main Causes of Slow DNS Lookups
Slow DNS lookups are typically the result of a combination of several small deficiencies, such as resolver quality, geographic routing, infrastructure limitations, and caching behavior.
After auditing hundreds of live websites and real user networks, these are the most common causes of high DNS latency across browsers, devices, and locations:
1. Internet Connection Problems
If your ISP is using a slow DNS server, this could be the biggest reason for slow DNS performance.
2. Distance and Network Latency
If your DNS server is in America and you are accessing it from India, it will naturally take more time. This is due to geographical distance.
3. Heavy Load on the DNS Server
Just like walking in a crowded place is slow, if the DNS server is receiving too many requests, the response will be slow.
4. Incorrect DNS Configuration
Sometimes, even a small mistake in the settings can cause a big problem.
5. Malware or Virus Attack
Malware can change your DNS settings and redirect you to fake websites. This is a serious security issue.
6. Low-quality or free DNS
Many domain registrars provide default DNS services that are slow, and people tend to use those low-performance services.
7. Too Many Unique Domains
Modern websites often load assets from numerous third-party domains, analytics, advertising, fonts, CDNs, widgets, which multiplies the DNS resolution time.
How to Check DNS Speed?
To understand the actual impact on users, DNS timing must be measured at the browser level, although many tools provide only average or simulated values.
There are three simple methods to check DNS speed:
1. Using Online Tools
You can measure your website’s DNS resolution speed using our free DNS checker tool, which will help you identify latency issues.
2. Using the Command Line (Windows Users)
nslookup -debug mozedia.com
This will show you how much time the DNS resolution is taking.
3. Using Chrome DevTools
- Open any website in Chrome
- Press F12 (Developer Tools)
- Go to the Network tab
- Hard Reload the page (
Ctrl + Shift + R) - Look at the “DNS Lookup” time in the first line
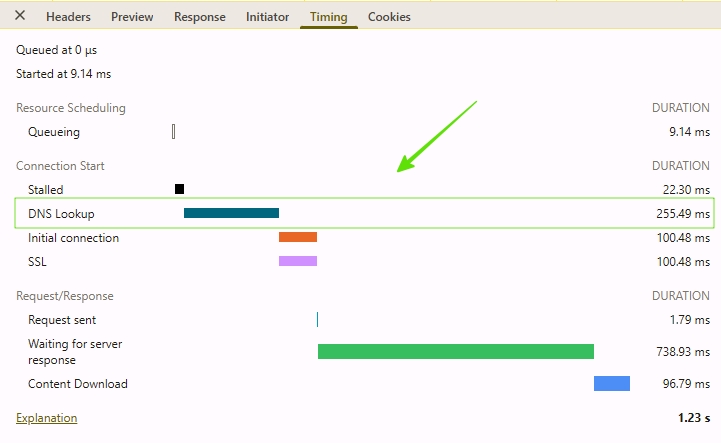
This method reflects real user experience, not synthetic or lab-based estimates, making it the most reliable way to diagnose DNS performance problems.
How to Fix Slow DNS Lookup – Proven Solutions 2026
To fix slow DNS lookups, immediately switch to a faster public DNS server in your network settings, such as Google (8.8.8.8) or Cloudflare (1.1.1.1).
Other effective, quick fixes include flushing your DNS cache, restarting your router, clearing browser data, and disabling unnecessary virtual network adapters.
We’ll explain each of these in detail below.
1. Switch to a Faster DNS Server
This is the easiest and most effective solution. Switching DNS resolvers is the single highest ROI optimization for DNS latency.
You can use Cloudflare free DNS,
Recommended resolvers:
Primary DNS: 8.8.8.8
Secondary DNS: 8.8.4.4
Google Public DNS is fast and reliable. It is used by users worldwide.
2. Cloudflare DNS (Best for Privacy)
Primary DNS: 1.1.1.1 Secondary DNS: 1.0.0.1
Cloudflare prioritizes privacy and also offers excellent speed.
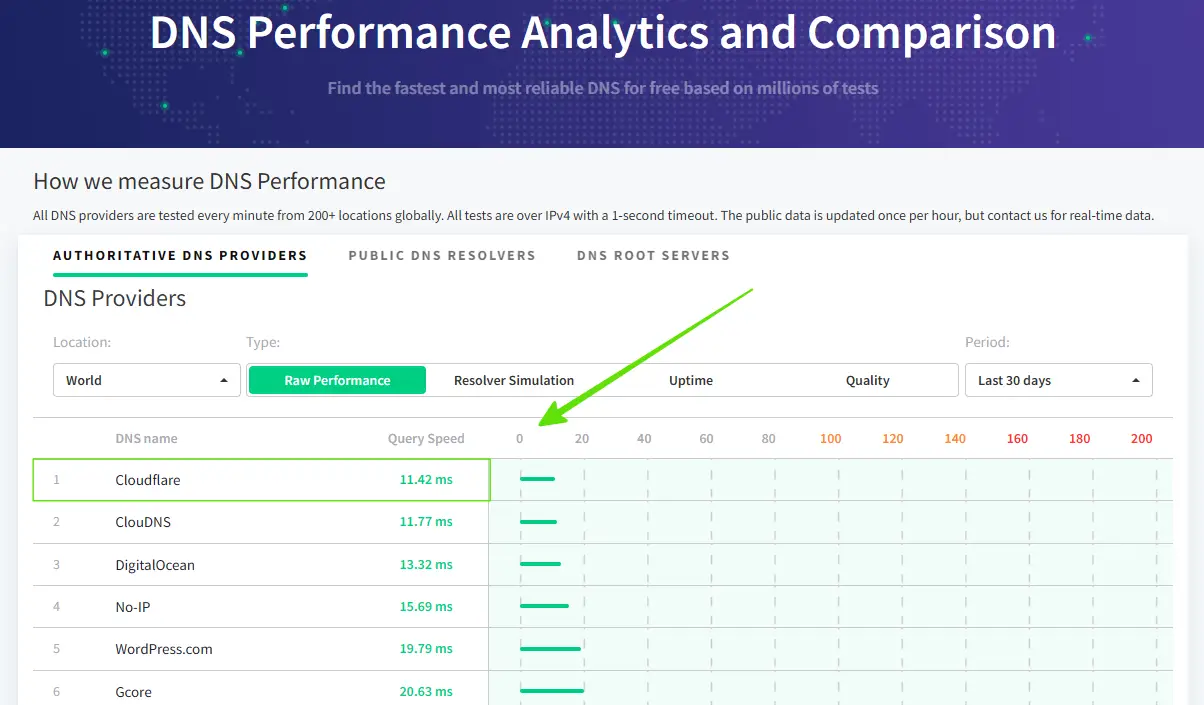
These providers use global Anycast routing, ensuring queries are answered by the nearest node. In many cases, this alone reduces DNS lookup time by 60–80%.
You can use Cloudflare’s free DNS service is widely regarded as one of the fastest DNS providers globally.
For example, see this DNS performance screenshot.
2. Flush the DNS Cache
The second solution is to flush DNS cache stores old records. Sometimes, this is the root of the problem, and regular flushing is necessary.
System-level DNS cache may continue serving slow or incorrect records.
Flush cache after:
- DNS provider changes
- CDN activation
- IP migrations
This forces fresh resolution and accurate testing.
How to flush DNS cache it in Windows:
1. Press Windows + R
2. Type cmd
3. Press Enter
4. Run this command: ipconfig /flushdns
How to flush DNS cache On Mac:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
How to flush DNS cache On Linux:
sudo systemd-resolve --flush-caches
3. Manually Configure DNS Settings
Manually configuring DNS settings provides greater control and reliability compared to automatic, ISP-assigned DNS resolution.
By explicitly defining trusted and high-performance DNS resolvers, you eliminate variability caused by network defaults and ensure consistent DNS behavior across sessions.
Steps for Windows 10/11:
- Open Settings
- Go to Network & Internet
- Click Change adapter options
- Right-click your active network connection and select Properties
- Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)
- Click the Properties button
- Choose Use the following DNS server addresses
- Enter a fast DNS resolver such as Google DNS or Cloudflare DNS
- Click OK to save the changes
4. Optimize Your Router Settings
Configuring DNS at the router level is a one-time optimization that improves DNS resolution speed for every device connected to the network.
Instead of relying on ISP-provided resolvers, the router forwards all DNS queries to a faster, globally optimized DNS provider, resulting in lower latency and more consistent performance.
Here are the steps for Router DNS setting:
- Enter your router’s IP address in a web browser (commonly 192.168.1.1)
- Log in to the router’s admin panel
- Navigate to the DNS or Internet settings section
- Replace the Primary and Secondary DNS addresses with Google DNS or Cloudflare DNS
- Save the changes and restart the router
Once applied, all connected devices automatically benefit from faster DNS resolution without requiring individual configuration.
5. Use Private DNS (Android Users)
Now, you think, what is private dns? Private DNS allows Android devices to send DNS queries over encrypted connections, improving privacy and protecting against DNS interception.
While its primary purpose is security, using a high-performance Private DNS provider can also result in more stable and consistent DNS resolution on supported networks.
This feature is available on Android 9 and later.
- Open Settings
- Go to Network & Internet
- Expand Advanced settings
- Tap on Private DNS
- Select Private DNS provider hostname
- Enter
dns.googleor1dot1dot1dot1.cloudflare-dns.com - Tap Save to apply the changes
After enabling Private DNS, the device will automatically use the selected provider for all DNS queries across mobile data and Wi-Fi networks.
6. Enable DNS Prefetching in the Browser
DNS prefetching is a lightweight optimization that allows the browser to resolve domain names in advance, before those resources are actually requested.
This reduces waiting time later in the loading process, especially for third-party domains such as fonts, analytics, and CDNs.
Add the following code inside the <head> section of your website’s HTML:
<!-- DNS prefetch for external resources -->
<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="//fonts.googleapis.com">
<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="//www.google-analytics.com">
<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="//cdn.example.com">
By using DNS prefetching, the browser performs DNS resolution early, so when the actual resource request is made, the connection can proceed immediately without additional lookup delays.
This technique should be used selectively for high-impact external domains to avoid unnecessary prefetching.
How to Reduce DNS Lookup in WordPress?
WordPress websites often generate a high number of DNS lookups due to plugins, themes, and third-party assets loaded from multiple external domains.
Each additional domain requires a separate DNS resolution, which increases initial page load time and negatively impacts performance.
Reducing DNS lookups in WordPress requires a combination of cleanup, proper asset handling, and smart configuration rather than a single setting change.
Below are practical, WordPress-specific solutions that work reliably in production environments.
1. Reduce the Number of DNS Lookups
The most common cause of excessive DNS lookups in WordPress is loading assets from many different domains, such as fonts, analytics scripts, ads, and external libraries.
Fonts, scripts, images, and tracking codes are often loaded from separate third-party domains, each triggering a new DNS lookup.
Solution:
- Remove unused plugins and scripts that load external resources
- Host fonts locally instead of loading them from Google Fonts
- Use a CDN such as Cloudflare to serve assets from a single optimized domain
Reducing even a few external domains can significantly lower total DNS resolution time.
2. Use a Proper Caching Plugin
Caching does not directly eliminate DNS lookups, but it reduces repeat requests and improves overall load consistency, making DNS latency less noticeable.
Recommended caching plugins:
- WP Rocket – paid, but highly effective and easy to configure
- W3 Total Cache – free and powerful, suitable for advanced users
- WP Super Cache – simple and beginner-friendly
A properly configured caching plugin reduces server load and improves perceived performance alongside DNS optimizations.
3. Use a DNS Prefetch Plugin
DNS prefetching helps the browser resolve external domains in advance, reducing delays when those resources are requested.
Instead of manually adding resource hints, WordPress users can use dedicated plugins that handle this automatically.
Recommended options:
- Perfmatters
- Pre Party Resource Hints
These plugins allow you to manage DNS prefetch and preconnect rules centrally, helping reduce DNS-related delays without touching theme files.
Here’s a detailed guide to speeding up WordPress; in this article, we’re also discussing DNS server optimization for WordPress.
Advanced Solutions of DNS Optimization
Once basic DNS issues are resolved, advanced website speed optimization can further reduce latency, improve reliability, and strengthen security.
These techniques are best suited for technical users, system administrators, and website owners managing production environments.
1. Set Up a Local DNS Resolver
Running a local DNS resolver such as Unbound allows DNS queries to be cached at the network or system level.
Instead of repeatedly querying external DNS servers, common domain records are served directly from the local cache.
Benefits of a local DNS resolver include:
- Faster DNS responses due to local caching
- Improved privacy by reducing external DNS queries
- Reduced dependency on upstream DNS resolvers
This approach is particularly effective in offices, development environments, or networks with multiple devices accessing the same websites repeatedly.
2. Optimize DNS TTL Values
If you manage your own DNS records, Time To Live (TTL) values play an important role in DNS performance and flexibility.
Recommended usage patterns:
- Short TTL (300–600 seconds) during migrations or frequent DNS changes
- Longer TTL (3600–86400 seconds) for stable, production-ready setups
A TTL of 3600 seconds (1 hour) is generally a good balance between performance and control, allowing changes to propagate reasonably fast without causing excessive DNS lookups.
3. Enable CNAME Flattening
Many modern DNS providers support CNAME flattening, which resolves CNAME records at the DNS level instead of requiring an additional lookup by the client.
By enabling CNAME flattening, extra DNS resolution steps are eliminated, reducing latency and simplifying DNS behavior. Providers such as Cloudflare offer this feature by default.
Best Tools to Measure DNS Latency
Accurate measurement is essential when diagnosing DNS performance issues. The following tools provide reliable DNS timing insights.
1. Pingdom Tools
Pingdom Tools is a simple yet powerful option for measuring DNS latency, especially when you want quick and clear insights.
You can see here DNS lookup time in pingdom tool.
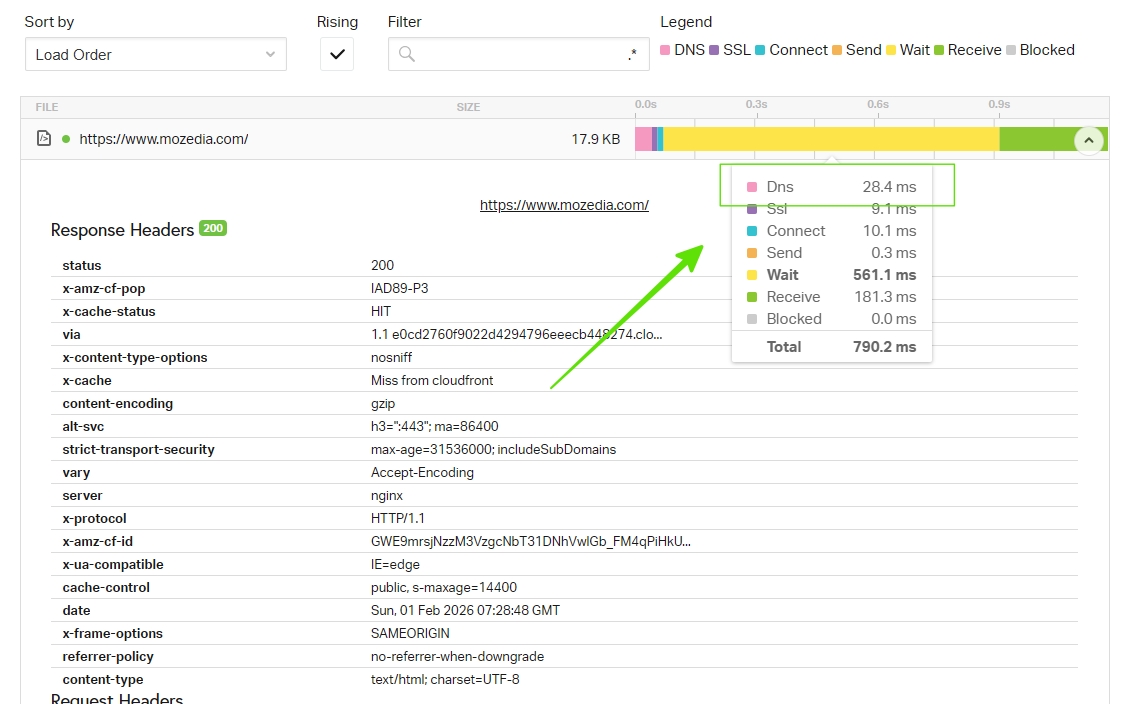
It breaks down DNS lookup time inside an easy-to-read waterfall chart and lets you test from multiple global locations, which helps identify whether delays are region-specific or DNS-server related.
Being free and fast, it’s ideal for quick diagnostics without technical complexity.
2. GTmetrix
GTmetrix goes a step further by clearly isolating DNS lookup time from other loading phases like connection, SSL, and content download.
This separation makes it easier to pinpoint DNS as the real bottleneck instead of guessing. You can find DNS lookup in gtmetrix waterfall section.
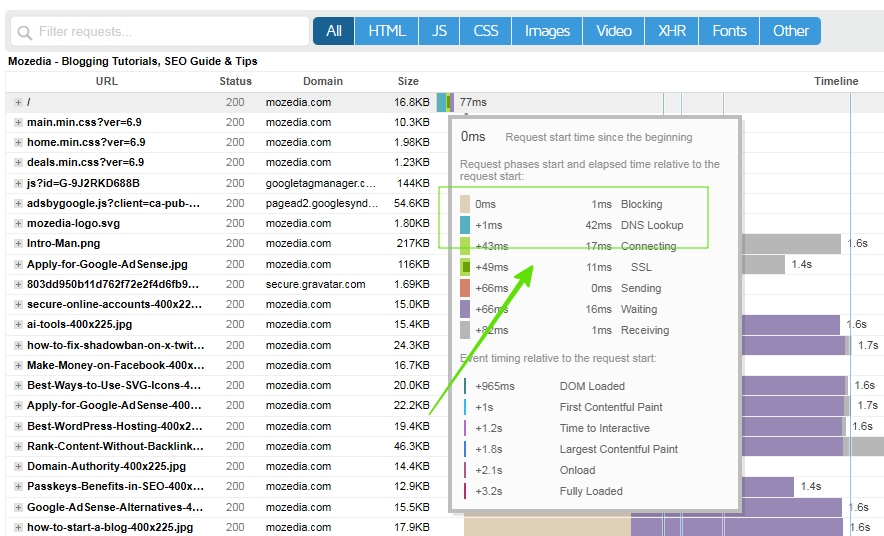
Along with timing data, it also provides performance recommendations, making it useful not just for analysis but for optimization decisions as well.
3. WebPageTest
WebPageTest is the most advanced tool among the three, designed for deep technical analysis.
It offers an extremely detailed request-level breakdown and visually highlights DNS lookup delays, helping you understand exactly how DNS impacts total page load time.
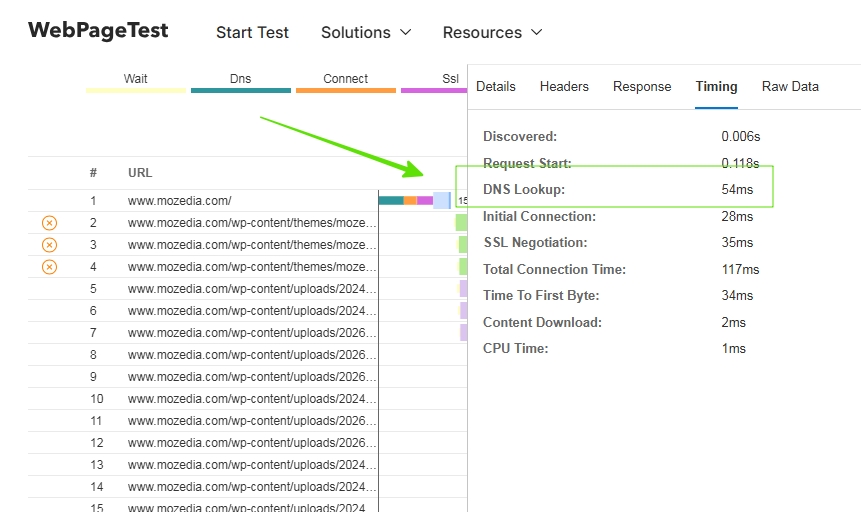
If you need precise, data-driven insights for serious performance tuning, this tool delivers unmatched clarity.
You can also leverage our free tools to measure, analyze, and optimize performance from multiple angles.
DNS Lookup Related FAQs
This section addresses the most common questions users have about DNS lookup, performance impact, security, and practical troubleshooting.
The answers are based on real-world usage and testing, focusing on clear explanations and actionable guidance rather than theoretical definitions.
What does flushing DNS do?
It clears stored DNS records and forces fresh resolution, often fixing connectivity and speed issues.
Is changing DNS safe
Yes. Trusted providers like Google and Cloudflare are widely used and reliable.
Will DNS changes increase internet speed
DNS does not increase bandwidth, but it reduces initial connection delays and improves browsing experience.
What is Private DNS
Private DNS encrypts DNS queries, improving privacy and protection against interception.
How often should DNS cache be flushed
Once a month is a good practice, or immediately when DNS-related issues occur.
Is changing DNS on the router better
Yes. It applies DNS improvements to all connected devices with a single configuration.
What is an ideal DNS lookup time
Below 50 ms is ideal. Anything above 200 ms requires immediate attention.
Are free DNS providers reliable
Yes. Providers like Google and Cloudflare are globally trusted and used by millions of users.
Our Recommendations
Fixing slow DNS lookup starts by using a fast and reliable DNS provider. A good DNS setup reduces connection delays and helps your website load faster.
Regular DNS maintenance is also important. Clearing the DNS cache after changes and using DNS prefetching can improve DNS resolution speed.
Key actions to fix slow DNS lookup:
- Use a fast, globally distributed DNS provider
- Flush DNS cache after updates or migrations
- Enable DNS prefetching where relevant
- Optimize DNS performance for mobile users
- Monitor DNS lookup times regularly
Slow DNS issues are more visible on mobile networks. Optimizing and regularly monitoring DNS helps maintain fast and consistent website performance.
Final Conclusion
Slow DNS lookups are a website performance issue that is often overlooked, but it’s a serious problem you should address.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, such as using a faster DNS provider, flushing your DNS cache, reducing unnecessary domains, and enabling DNS prefetching, you can effectively understand and fix slow DNS lookup issues.
DNS optimization isn’t a one-time task. Regular monitoring, performance testing, and DNS tuning ensure that your website remains consistently fast.


